<?php
$a = 1;
if ($a < 5) {
echo '<div style="background-color: red">
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<h2>No estás autorizado a entrar</h2>
</div>';
} elseif ($a < 10) {
echo "Menor de 10";
} elseif ($a < 20) {
echo "Menor de 20";
} else {
echo "Mayor de 20";
}
switch ($a) {
case 1:
echo "Vale uno";
break;
case 2:
case 3:
echo "Vale 2 o 3";
break;
default:
echo "Vale más de tres";
}
?>
PHP if
<?php
$a = 1;
if ($a < 5) {
echo '<div style="background-color: red">
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<h2>No estás autorizado a entrar</h2>
</div>';
} else {
echo "Mayor de 5";
}
if ($a < 5) {
?>
<div style="background-color: red">
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<h2>No estás autorizado a entrar</h2>
</div>
<?php
} else {
?>
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<?php
}
if ($a < 5):
?>
<div style="background-color: red">
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<h2>No estás autorizado a entrar</h2>
</div>
<?php
else:
?>
<h2>Menor de 5</h2>
<?php
endif
?>
Ejemplos create view
Primero creamos una vista base:
create view country_payment as select country, payment.* from country join city using (country_id) join address using (city_id) join customer using (address_id) join payment using (customer_id)
Después nos basamos en esta para crear las siguientes:
create view country_total as select country, sum(amount) total from country_payment group by country create view country_month as select country, month(payment_date) month, count(payment_id) total from country_payment group by country, month
Integrar Moodle y WordPress
Publicar WordPress en un servidor desde local
Para publicar WP en un servidor necesitamos hacer varias cosas:
– Subir los archivos
– Subir la base de datos
– Configurar el WP
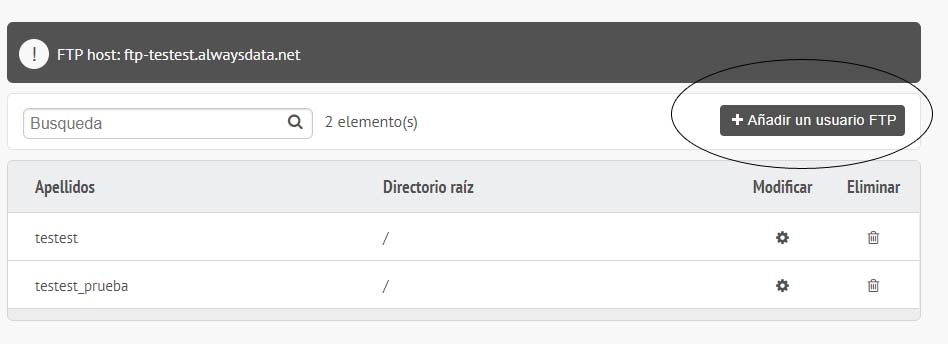
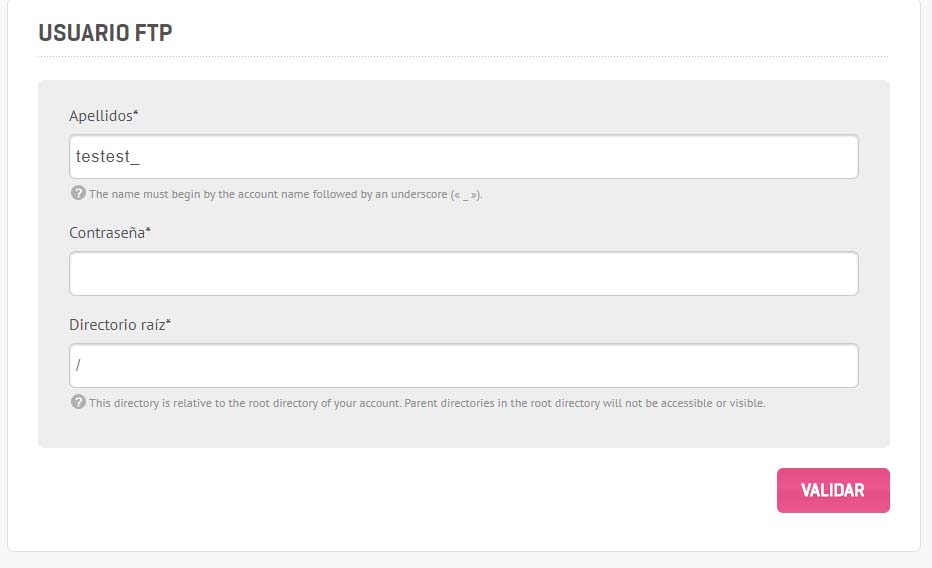
Para subir los archivos necesitamos una cuenta ftp. En el caso de always data se crea así:
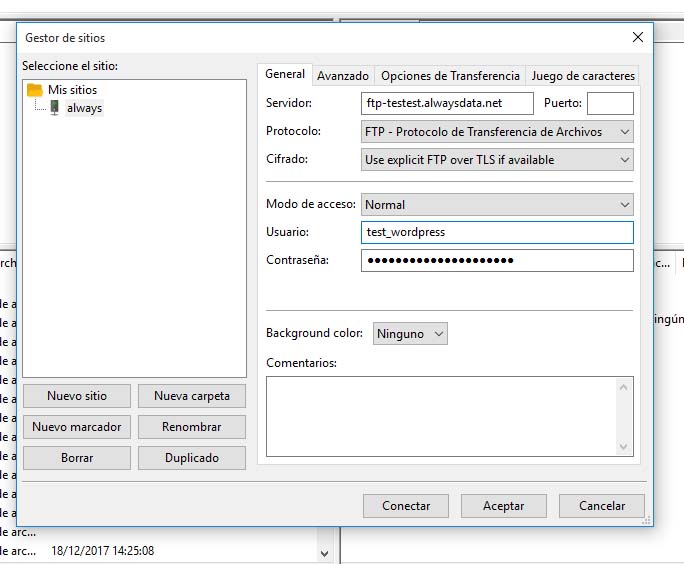
Con esta cuenta nos iremos a cualquier programa cliente de ftp, por ejemplo filezilla, y configuramos la cuenta ftp:
Una vez hecho esto y conectados a la cuenta sólo tenemos que arrastrar los archivos a la carpeta www del servidor.
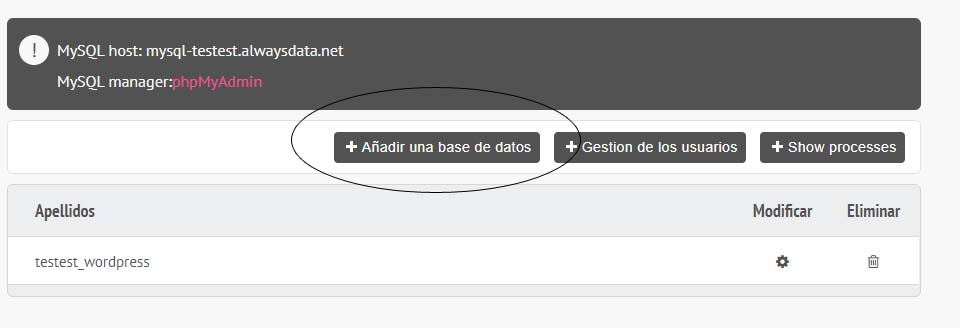
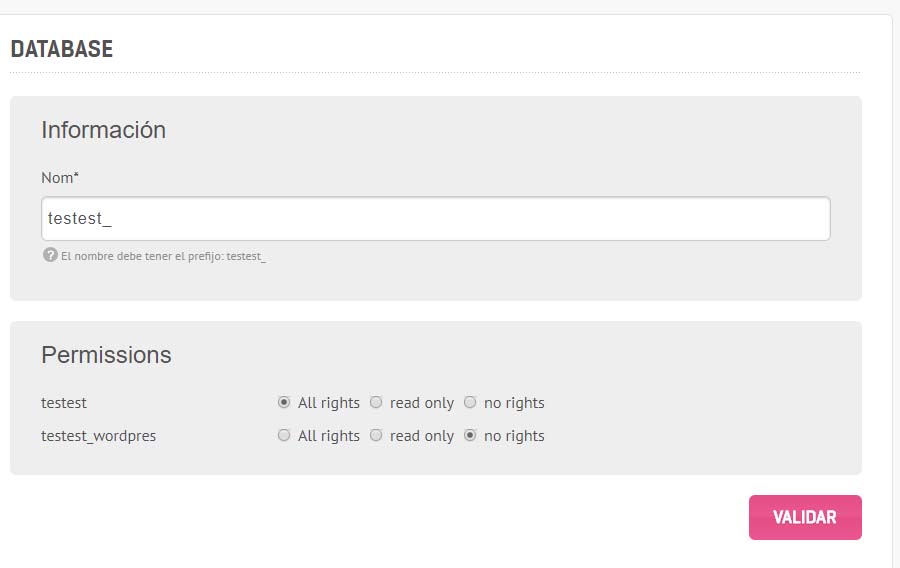
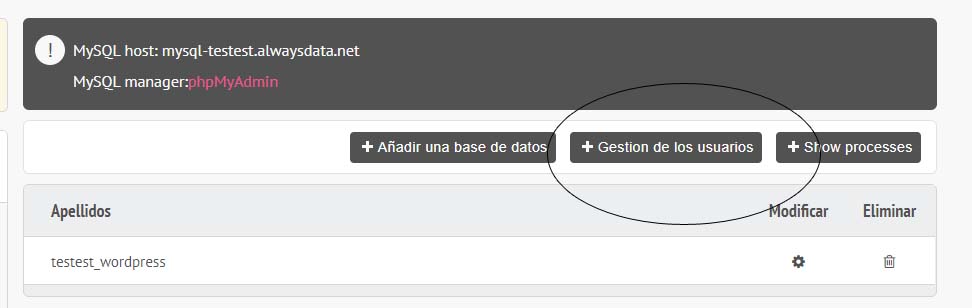
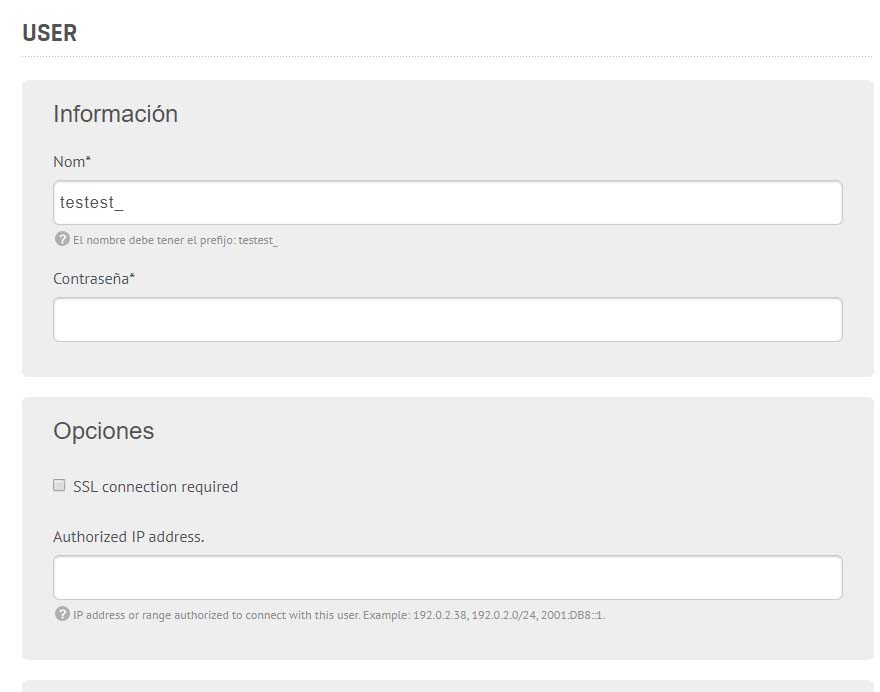
Para subir la base de datos tenemos que crear una base de datos en el servidor, y después exportar en local e importar en remoto:
Creamos la base de datos:
Creamos el usuario:
En localhost/phpmyadmin (http://localhost/phpmyadmin/) exportamos la base de datos:
En phpmyadmin de alwaysdata (https://phpmyadmin.alwaysdata.com/), entrando con nuestro usuario, le damos a importar
Ejercicios Base de datos
Total de pagos por países
select country, sum(amount) total from
country join city using (country_id)
join address using (city_id)
join customer using (address_id)
join payment using (customer_id)
group by country
Películas con más de diez actores
select title, count(actor_id) actores
from film join film_actor using (film_id)
group by title
having actores>10
Actor que ha trabajado en más películas
select first_name, last_name, count(film_id) peliculas
from actor join film_actor using(actor_id)
group by first_name, last_name
order by peliculas desc
limit 0,1
Actores que han hecho películas de acción
select distinct first_name, last_name,name
from actor join film_actor using(actor_id)
join film using(film_id)
join film_category using(film_id)
join category using(category_id)
where name=’Action’
order by first_name,last_name
Países con más de 50 clientes
select country, count(customer_id) total from
country join city using (country_id)
join address using (city_id)
join customer using (address_id)
group by country
having total>50