<?php
$a = 3;
$b = 3;
if ($a > $b * 2) {
echo 'a es mucho mayor que b';
} elseif ($a > $b) {
echo 'a es mayor que b';
} elseif ($a * 2 < $b) {
echo 'a es mucho menor que b';
} elseif ($a < $b) {
echo 'a es menor que b';
} else {
echo 'iguales';
}
echo 'hola que tal';
if ($a) {
}
?>
<hr/>
<?php
$a = 1;
while ($a ** 3 < 1000) {
echo ($a ** 3) . "<br/>";
$a++;
}
?>
<hr/>
<?php
for ($i = 1; $i < 100; $i*=2) {
echo $i . "<br/>";
}
$tabla = array('Ana', 'Juan', 'Rosa');
foreach ($tabla as $nombre) {
echo $nombre . "<br/>";
}
?>
<hr/>
<?php
$tabla = 5;
//Imprimiendo el HTML
echo "<table border=1>";
for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; $i++) {
echo "<tr><td>$i</td><td>x</td><td>$tabla</td><td>" . ($i * $tabla) . "</td></tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
//Mezclando HTML y PHP. Recordemos que <?= es equivalente a <?php echo
?>
<table border=1>
<?php
for ($i = 1; $i <= 10; $i++) {
?>
<tr><td><?= $i ?></td><td>x</td><td><?= $tabla ?></td><td><?= ($i * $tabla) ?></td></tr>
<?php
}
?>
</table>
Primeros pasos en PHP
<?php $a=2; $b=3; echo "suma: \n"; echo $a+$b; //Muestra 5 echo "<br/>concatenar: "; echo $a.$b; //Muestra 23 ?> <hr/> <?php $a=5; $b=4.2; $d=false; $e="7up"; echo $a+$e; echo gettype($a); echo "<br/>"; echo gettype($b); echo "<br/>"; echo gettype($d); echo "<br/>"; echo gettype($e); echo "<br/>"; ?> <hr/> <?php $a=5; $b=true; echo "#".($a==$b)."#"; echo "<br/>"; echo "#".($a===$b)."#"; ?>
Crear funciones
Ejemplos:
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost`
FUNCTION `inventory_in_stock`(p_inventory_id INT)
RETURNS tinyint(1)
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
DECLARE v_rentals INT;
DECLARE v_out INT;
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_rentals
FROM rental
WHERE inventory_id = p_inventory_id;
IF v_rentals = 0 THEN
RETURN TRUE;
END IF;
SELECT COUNT(rental_id) INTO v_out
FROM inventory LEFT JOIN rental USING(inventory_id)
WHERE inventory.inventory_id = p_inventory_id
AND rental.return_date IS NULL;
IF v_out > 0 THEN
RETURN FALSE;
ELSE
RETURN TRUE;
END IF;
END
select inventory_in_stock(30)
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost`
FUNCTION `clientes_por_pais`
(p_country varchar(50)) RETURNS int(11)
BEGIN
declare total int;
SELECT count(customer_id) into total
FROM sakila.country
left join city using (country_id)
left join address using (city_id)
left join customer using (address_id)
where country=p_country
group by country;
RETURN total;
END
select clientes_por_pais('Algeria')
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` FUNCTION `peliculas_por_actor`(p_actor_id int) RETURNS int(11)
BEGIN
declare total int;
select count(film_id) into total from film join
film_actor using (film_id)
join actor using(actor_id)
where actor.actor_id=p_actor_id;
RETURN total;
END
select peliculas_por_actor(1)
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost`
FUNCTION `total_ventas`() RETURNS decimal(10,2)
BEGIN
declare total decimal(10,2);
select sum(amount) into total from payment;
RETURN total;
END
Sql views
create or replace view cliente_gaston as select customer.customer_id first_name, last_name, sum(amount) as total from customer join payment using(customer_id) group by first_name, last_name order by total desc limit 0,5
update customer set active=5 where customer_id in (select customer_id from cliente_gaston)
Tutoriales programación (con escote)
10 page sliders con jquery
http://www.sitepoint.com/10-jquery-sliding-sidebar-panel-plugins/
Más SQL
Países con tiendas:
select country, count(store_id) as total from country left join city using (country_id) left join address using (city_id) left join store using (address_id) group by country having total>0
Cliente que más gasta:
select first_name, last_name, sum(amount) as total from customer join payment using(customer_id) group by first_name, last_name order by total desc limit 0,1
Ejemplos de CASE e IF:
SELECT *, case when amount<1 then 'barato' when amount between 1 and 3 then 'medio' else 'caro' end precio, if (amount<3,'barato','caro') precio2 FROM sakila.payment;
Con funciones de agregado:
select first_name, last_name, sum(amount) as total, if (sum(amount)>100,'gastador','rácano') tipo from customer join payment using(customer_id) group by customer_id
Pagos formateados:
SELECT lpad(format(amount,3),10,' ') from payment
Nombre formateado y ordenar por longitud de apellido:
select ucase(first_name), lcase(last_name), concat( ucase(substring(first_name,1,1)), lcase(substring(first_name,2)) ) cliente, length(last_name) longitud from customer order by longitud desc
Sentencias sql
Clientes que se llaman igual que actores de películas
SELECT distinct concat(c.first_name, " ", c.last_name) cliente, concat(a.first_name, " ", a.last_name) as actor FROM actor a join film_actor using (actor_id) join film using (film_id) join inventory using (film_id) join rental using (inventory_id) join customer c using (customer_id) where a.first_name=c.first_name order by cliente
Películas por categoría:
select name, count(title) from category join film_category using(category_id) join film using (film_id) group by name
Clientes por país:
SELECT country, count(customer_id) FROM sakila.country left join city using (country_id) left join address using (city_id) left join customer using (address_id) group by country;
Clientes que se apellidan como el empleado que los atiende:
select distinct concat(c.first_name, " ", c.last_name) cliente, concat(s.first_name, " ", s.last_name) as empleado from customer c join rental using (customer_id) join staff s using (staff_id) where c.last_name=s.last_name
Clientes que viven en el mismo código postal que los empleados:
select distinct concat(c.first_name, " ", c.last_name) cliente, concat(s.first_name, " ", s.last_name) as empleado from customer c join address a1 on c.address_id=a1.address_id join address a2 on a1.postal_code=a2.postal_code join staff s on a2.address_id=s.address_id
Películas con importe total de alquiler menor que 2:
select title, avg(ifnull(amount,0)) total from film left join inventory using (film_id) left join rental using (inventory_id) left join payment using (rental_id) group by title having total<2 order by 2
Total de clientes por países
select country, count(customer_id) from country join city using (country_id) join address using (city_id) join customer using (address_id) group by country
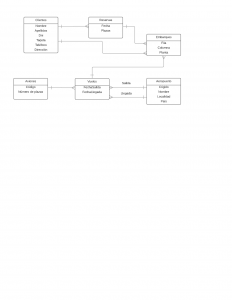
Modelo ER ejercicio vuelos
¿Claves primarias naturales o artificiales?
Aquí un hilo interesante:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/337503/whats-the-best-practice-for-primary-keys-in-tables